1.
Refer to the exhibit. What two statements can be concluded from the information that is shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
• All ports that are listed in the exhibit are access ports.
• ARP requests from Host1 will be forwarded to Host2.
• Attaching Host1 to port 3 will automatically allow communication between both hosts.
• The default gateway for each host must be changed to 192.168.3.250/28 to allow communication between both hosts.
• A router connected to the switch is needed to forward traffic between the hosts.
2.

A router is configured to connect to a trunked uplink as shown in the exhibit. A packet is received on the FastEthernet 0/1 physical interface from VLAN 10. The packet destination address is 192.168.1.120. What will the router do with this packet?
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.1 tagged for VLAN 10.
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2 tagged for VLAN 60.
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3 tagged for VLAN 60.
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3 tagged for VLAN 120.
• The router will not process the packet since the source and destination are on the same subnet.
• The router will drop the packet since no network that includes the source address is attached to the router.

A router is configured to connect to a trunked uplink as shown in the exhibit. A packet is received on the FastEthernet 0/1 physical interface from VLAN 10. The packet destination address is 192.168.1.120. What will the router do with this packet?
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.1 tagged for VLAN 10.
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2 tagged for VLAN 60.
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3 tagged for VLAN 60.
• The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3 tagged for VLAN 120.
• The router will not process the packet since the source and destination are on the same subnet.
• The router will drop the packet since no network that includes the source address is attached to the router.
3. The information contained in a BPDU is used for which two purposes? (Choose two.)
• to prevent loops by sharing bridging tables between connected switches
• to set the duplex mode of a redundant link
• to determine the shortest path to the root bridge
• to determine which ports will forward frames as part of the spanning tree
• to activate looped paths throughout the network
• to prevent loops by sharing bridging tables between connected switches
• to set the duplex mode of a redundant link
• to determine the shortest path to the root bridge
• to determine which ports will forward frames as part of the spanning tree
• to activate looped paths throughout the network
4. A router has two serial interfaces and two Fast Ethernet interfaces. This router must be connected to a WAN link and to a switch that supports four VLANs. How can this be accomplished in the most efficient and cost-effective manner to support inter-VLAN routing between the four VLANs?
• Connect a smaller router to the serial interface to handle the inter-VLAN traffic.
• Add two additional Fast Ethernet interfaces to the router to allow one VLAN per interface.
• Connect a trunked uplink from the switch to one Fast Ethernet interface on the router and create logical subinterfaces for each VLAN.
• Use serial-to-Fast Ethernet transceivers to connect two of the VLANs to the serial ports on the router. Support the other two VLANs directly to the available FastEthernet ports.
• Connect a smaller router to the serial interface to handle the inter-VLAN traffic.
• Add two additional Fast Ethernet interfaces to the router to allow one VLAN per interface.
• Connect a trunked uplink from the switch to one Fast Ethernet interface on the router and create logical subinterfaces for each VLAN.
• Use serial-to-Fast Ethernet transceivers to connect two of the VLANs to the serial ports on the router. Support the other two VLANs directly to the available FastEthernet ports.
5. When are MAC addresses removed from the CAM table?
• at regular 30 second intervals
• when a broadcast packet is received
• when the IP Address of a host is changed
• after they have been idle for a certain period of time
• at regular 30 second intervals
• when a broadcast packet is received
• when the IP Address of a host is changed
• after they have been idle for a certain period of time
6.
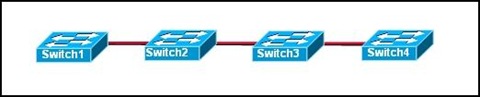
Refer to the exhibit. Switch1 is not participating in the VTP management process with the other switches. Which two are possible reasons for this? (Choose two.)
• Switch2 is in transparent mode.
• Switch1 is in client mode.
• Switch1 is using VTP version 1 and Switch2 is using VTP version 2.
• Switch2 is in server mode.
• Switch1 is in a different management domain.
• Switch1 has no VLANs.

Refer to the exhibit. Switch1 is not participating in the VTP management process with the other switches. Which two are possible reasons for this? (Choose two.)
• Switch2 is in transparent mode.
• Switch1 is in client mode.
• Switch1 is using VTP version 1 and Switch2 is using VTP version 2.
• Switch2 is in server mode.
• Switch1 is in a different management domain.
• Switch1 has no VLANs.
7. Which three must be used when a router interface is configured for VLAN trunking? (Choose three.)
• one subinterface per VLAN
• one physical interface for each subinterface
• one IP network or subnetwork for each subinterface
• one trunked link per VLAN
• a management domain for each subinterface
• a compatible trunking protocol encapsulation for each subinterface
• one subinterface per VLAN
• one physical interface for each subinterface
• one IP network or subnetwork for each subinterface
• one trunked link per VLAN
• a management domain for each subinterface
• a compatible trunking protocol encapsulation for each subinterface
Refer to the exhibit. The switches are connected with trunks within the same VTP management domain. Each switch is labeled with its VTP mode. A new VLAN is added to Switch3. This VLAN does not show up on the other switches. What is the reason for this?
• VLANs cannot be created on transparent mode switches.
• Server mode switches neither listen to nor forward VTP messages from transparent mode switches.
• VLANs created on transparent mode switches are not included in VTP advertisements.
• There are no ports assigned to the new VLAN on the other switches.
• Transparent mode switches do not forward VTP advertisements.
9. Which two criteria are used by STP to select a root bridge? (Choose two.)
• memory size
• bridge priority
• switching speed
• number of ports
• base MAC address
• switch location
• memory size
• bridge priority
• switching speed
• number of ports
• base MAC address
• switch location
10. Which three steps should be taken before moving a Catalyst switch to a new VTP management domain? (Choose three.)
• Reboot the switch.
• Reset the VTP counters to allow the switch to synchronize with the other switches in the domain.
• Download the VTP database from the VTP server in the new domain.
• Configure the VTP server in the domain to recognize the BID of the new switch.
• Select the correct VTP mode and version.
• Configure the switch with the name of the new management domain.
• Reboot the switch.
• Reset the VTP counters to allow the switch to synchronize with the other switches in the domain.
• Download the VTP database from the VTP server in the new domain.
• Configure the VTP server in the domain to recognize the BID of the new switch.
• Select the correct VTP mode and version.
• Configure the switch with the name of the new management domain.
11. Which two items will prevent broadcasts from being sent throughout the network? (Choose two.)
• bridges
• routers
• switches
• VLANs
• hubs
• bridges
• routers
• switches
• VLANs
• hubs
12. Which two characteristics describe a port in the STP blocking state? (Choose two.)
• provides port security
• displays a steady green light
• learns MAC addresses as BPDUs are processed
• discards data frames received from the attached segment
• receives BPDUs and directs them to the system module
• provides port security
• displays a steady green light
• learns MAC addresses as BPDUs are processed
• discards data frames received from the attached segment
• receives BPDUs and directs them to the system module
13. What is the first step in the process of convergence in a spanning tree topology?
• election of the root bridge
• determination of the designated port for each segment
• blocking of the non-designated ports
• selection of the designated trunk port
• activation of the root port for each segment
• election of the root bridge
• determination of the designated port for each segment
• blocking of the non-designated ports
• selection of the designated trunk port
• activation of the root port for each segment
14. In which STP state does a switch port transmit user data and learn MAC addresses?
• blocking
• learning
• disabling
• listening
• forwarding
• blocking
• learning
• disabling
• listening
• forwarding
15. What is the purpose of VTP?
• maintaining consistency in VLAN configuration across the network
• routing frames from one VLAN to another
• routing the frames along the best path between switches
• tagging user data frames with VLAN membership information
• distributing BPDUs to maintain loop-free switched paths
• maintaining consistency in VLAN configuration across the network
• routing frames from one VLAN to another
• routing the frames along the best path between switches
• tagging user data frames with VLAN membership information
• distributing BPDUs to maintain loop-free switched paths
16. Which statement best describes adaptive cut-through switching?
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using cut-through switching and then changes to store-and-forward switching if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using cut-through switching and then changes to fast-forward switching if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using cut-through switching and then temporarily disables the port if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using store-and-forward switching and then changes to cut-through switching if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using cut-through switching and then changes to store-and-forward switching if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using cut-through switching and then changes to fast-forward switching if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using cut-through switching and then temporarily disables the port if errors exceed a threshold value.
• The switch initially forwards all traffic using store-and-forward switching and then changes to cut-through switching if errors exceed a threshold value.
17. Using STP, how long does it take for a switch port to go from the blocking state to the forwarding state?
• 2 seconds
• 15 seconds
• 20 seconds
• 50 seconds
• 2 seconds
• 15 seconds
• 20 seconds
• 50 seconds
18.
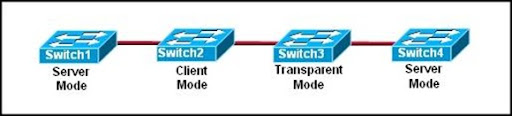
Refer to the exhibit. The switches are interconnected by trunked links and are configured for VTP as shown. A new VLAN is added to Switch1. Which three actions will occur? (Choose three.)
• Switch1 will not add the VLAN to its database and will pass the update to Switch 2.
• Switch2 will add the VLAN to its database and pass the update to Switch3.
• Switch3 will pass the VTP update to Switch4.
• Switch3 will add the VLAN to its database.
• Switch4 will add the VLAN to its database.
• Switch4 will not receive the update.

Refer to the exhibit. The switches are interconnected by trunked links and are configured for VTP as shown. A new VLAN is added to Switch1. Which three actions will occur? (Choose three.)
• Switch1 will not add the VLAN to its database and will pass the update to Switch 2.
• Switch2 will add the VLAN to its database and pass the update to Switch3.
• Switch3 will pass the VTP update to Switch4.
• Switch3 will add the VLAN to its database.
• Switch4 will add the VLAN to its database.
• Switch4 will not receive the update.
19. Which Catalyst feature causes a switch port to enter the spanning-tree forwarding state immediately?
• backbonefast
• uplinkfast
• portfast
• rapid spanning tree
• backbonefast
• uplinkfast
• portfast
• rapid spanning tree
20.

Refer to the exhibit. Which set of commands would be used on the router to provide communication between the two hosts connected to the switch?
• Router(config)# interface vlan 2
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config)# interface vlan 3
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
• Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0.2
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 2
Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0.3
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 3
Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
• Router(config)# interface vlan 2
Router(config-if)# switchport mode trunk dot1q
Router(config)# interface vlan 3
Router(config-if)# switchport mode trunk dot1q
• Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)# mode trunk dot1q 2 3
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0v

Refer to the exhibit. Which set of commands would be used on the router to provide communication between the two hosts connected to the switch?
• Router(config)# interface vlan 2
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config)# interface vlan 3
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
• Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0.2
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 2
Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0.3
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 3
Router(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
• Router(config)# interface vlan 2
Router(config-if)# switchport mode trunk dot1q
Router(config)# interface vlan 3
Router(config-if)# switchport mode trunk dot1q
• Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)# mode trunk dot1q 2 3
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0v

